Glycogen in the liver
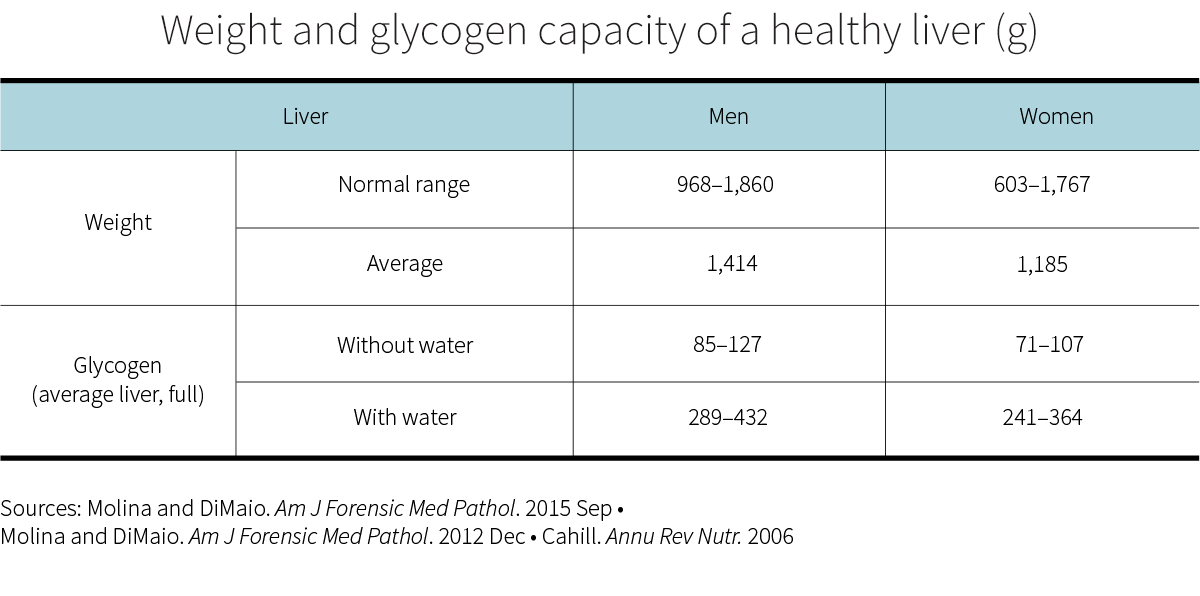
Your body uses your liver for short-term storage of glycogen. When you fast (which most of you do overnight as you sleep), your liver is where your brain will first search for the glucose it needs to keep functioning. After a fast of 12–16 hours, when liver stores are 25–50% depleted, each kilogram of the average liver still contains 44 grams of glycogen (range: 14–80 g),[1] so we can estimate the maximal capacity of the average liver at 60–90 g/kg.
Glycogen, moreover, cannot be stored on its own: it must be bound to water. In your liver, each gram of glycogen comes along with 2.4 grams of water.[2]
When full of glycogen, the average, healthy, human-male liver is heavier by 289–432 grams (0.6–1.0 lb), whereas the average, healthy, human-female liver is heavier by 241–364 grams (0.5–0.8 lb).
Glycogen in the muscles
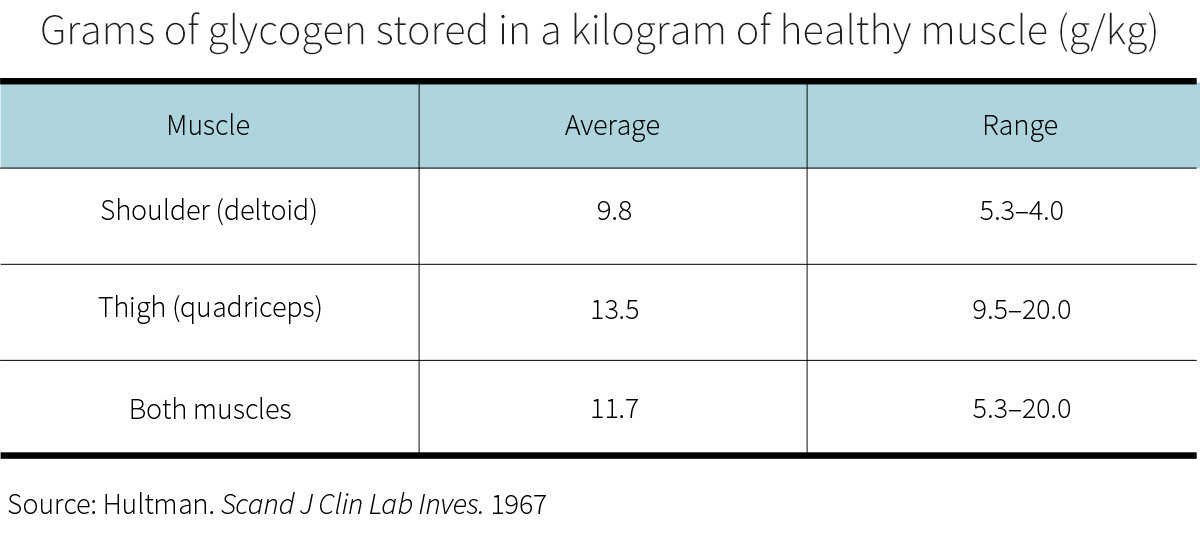
Glycogen also gets stored in your muscles.
 [5]
[5]
Of course, typical muscle mass varies greatly between individual men (22–40 kg, typically) and women (15–30 kg).[6] By combining those numbers with an estimation of the muscles’ average glycogen content (11.7 g/kg), we can further estimate that, in their muscles, men carry 256–466 grams of glycogen, and women 175–350 grams.
As we saw however, glycogen cannot be stored on its own: it must be bound to water. In your muscles, each gram of glycogen comes along with at least 3 grams of water,[7] which can become 17 grams if you co-ingest a lot of fluid and a lot of carbs after exercising in a hot, dry environment.[7]
Therefore, in normal circumstances, a man who carries 31 kilograms of muscles (68 lb) also carries in those muscles 361 grams of glycogen and 1,083 grams of water (0.8 and 2.4 lb). And if he drinks a lot while ingesting his carbs, as is often the case during a feast, he may end up carrying much more.
Likewise, in normal circumstances, a woman who carries 23 kilograms of muscles (51 lb) also carries in those muscles 268 grams of glycogen and 804 grams of water (0.6 and 1.8 lb). And if she drinks a lot while ingesting her carbs, as is often the case during a feast, she may end up carrying much more.
If you drink a lot and ingest a lot of carbs, as is likely during a feast, your muscles might gain several pounds of water weight.
Glycogen depletion
Compared to sedentary people, athletes have more muscle and can better synthesize and store glycogen.[8][9] A small study found the maximal storage capacity of its subjects (three male collegiate athletes) to be 629–1,146 grams, with an average of 810 grams.[10] That’s way more than the 341–593 grams (85–127 in the liver, 256–466 in the muscles, as we saw previously) carried by the average man.
Note that, to reach those numbers, the athletes followed a specific protocol: the first three days, they depleted their glycogen stores with exercise and a low-carbohydrate diet; then, for each of the next seven days, they consumed 3,500–5,000 calories, of which 80–90% came from carbs (760–990 grams). On the first day of this week-long binge, all the extra energy served to refill glycogen stores; the athletes didn’t gain any fat. On the second day, fat synthesis amounted to only 30 grams. On the third day, to only 45 grams.
At the end of this week-long binge, the athletes had gained 4.6 kg (10.1 lb) on average, of which 1.1 kg (2.5 lb) was fat. Only half of this fat came from the enormous amount of carbs consumed; the other half came from the proportionally little fat consumed.
Glycogen depletion through diet and exercise on the days leading to a feast can help buffer the caloric load of any carbohydrates being eaten, and therefore help minimize fat gain.
Examine Database: Glycogen
| Intervention | Grade | Effect | Detail |
|---|---|---|---|
| High-Carbohydrate Diet | D | ||
| Creatine | B | ||
| Resveratrol | D | ||
Create a free account to unlock more rows for free. Or unlock everything with an Examine+ free trial. | |||
| Chromium | |||
Research FeedRead all studies
In this meta-analysis of 20 studies in 180 participants, resistance exercise reduced muscle glycogen, and the size of the reduction increased as the workout duration and number of sets increased.
References
Examine Database References
- Chromium - Volek JS, Silvestre R, Kirwan JP, Sharman MJ, Judelson DA, Spiering BA, Vingren JL, Maresh CM, Vanheest JL, Kraemer WJEffects of chromium supplementation on glycogen synthesis after high-intensity exerciseMed Sci Sports Exerc.(2006 Dec)
- Creatine - Op 't Eijnde B, Ursø B, Richter EA, Greenhaff PL, Hespel PEffect of oral creatine supplementation on human muscle GLUT4 protein content after immobilizationDiabetes.(2001 Jan)
- Resveratrol - Scribbans TD, Ma JK, Edgett BA, Vorobej KA, Mitchell AS, Zelt JG, Simpson CA, Quadrilatero J, Gurd BJResveratrol supplementation does not augment performance adaptations or fibre-type-specific responses to high-intensity interval training in humansAppl Physiol Nutr Metab.(2014 Nov)
- Creatine - Nelson AG, Arnall DA, Kokkonen J, Day R, Evans JMuscle glycogen supercompensation is enhanced by prior creatine supplementationMed Sci Sports Exerc.(2001 Jul)
- High-Carbohydrate Diet - Solem K, Clauss M, Jensen JGlycogen supercompensation in skeletal muscle after cycling or running followed by a high carbohydrate intake the following days: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Front Physiol.(2025)