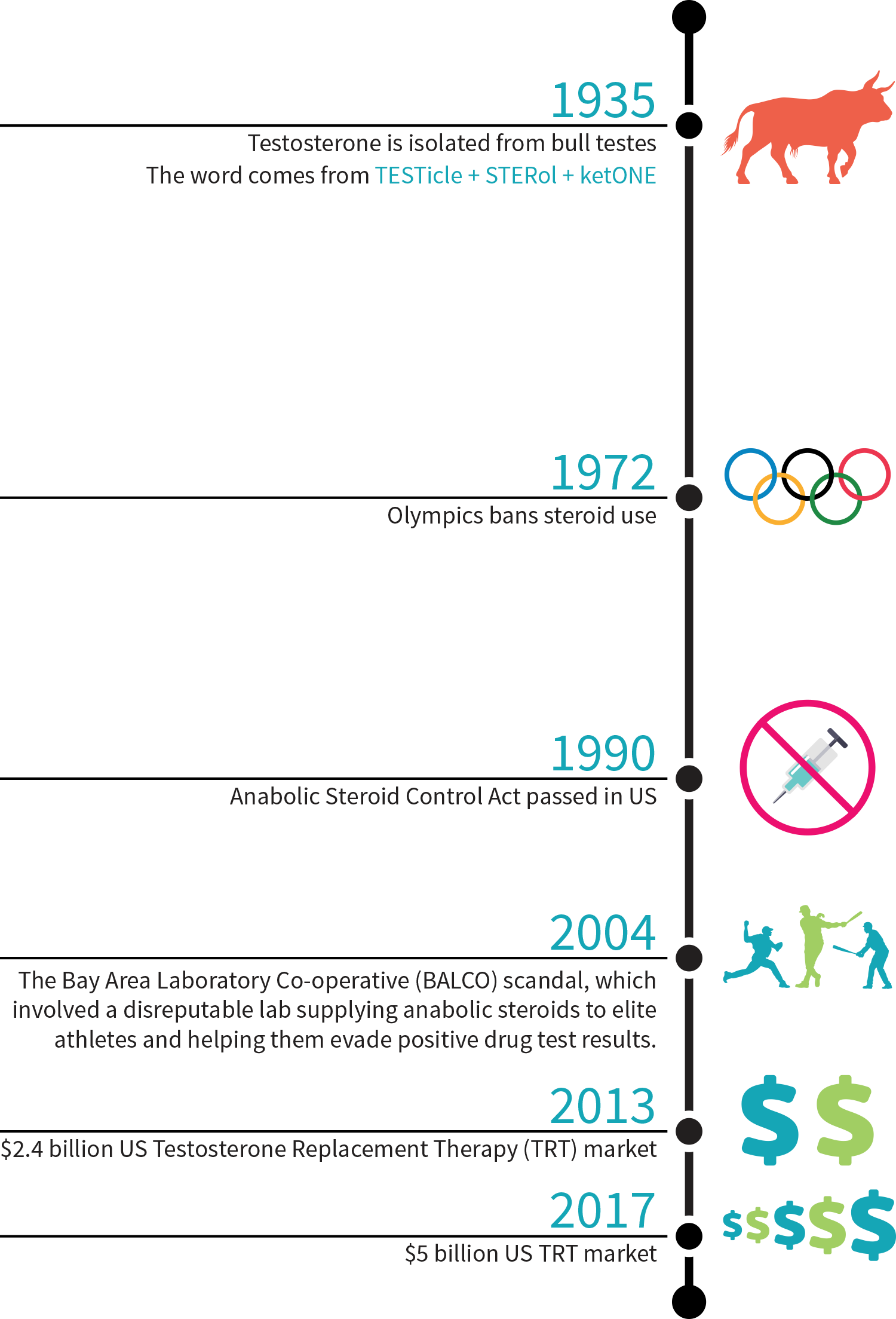
Overview
Testosterone is a hormone produced primarily in the testes in men and the ovaries in women. Testosterone is connected to sexual development, muscle building, fat loss, some aspects of cognition, and hair loss.[1]
Your testosterone levels may not tell the whole story of how testosterone is functioning in your body. Total testosterone can be divided into three categories.[2]
- Tightly bound testosterone: About two-thirds of the testosterone in your blood is bound to sex hormone binding globulin (SHBG). It is not readily available for use by your body.
- Loosely bound testosterone: About one-third of the testosterone in your blood is weakly bound to albumin. Once the bond is broken, the testosterone circulates as free testosterone in your body.
- Free testosterone: A small percentage of the testosterone in your blood (1–4%, as a rule) floats around freely. Your body can readily use it, and the enzyme 5-alpha-reductase can convert it to dihydrotestosterone (DHT), a very potent androgen.
Together, your loosely bound and free testosterone compose your bioavailable testosterone, which has a greater impact on your health than your total testosterone.
How are testosterone levels assessed?
A blood test is used to assess testosterone and its components (free T, bound T, etc). Abnormally low or high levels can cause health issues in males and females.
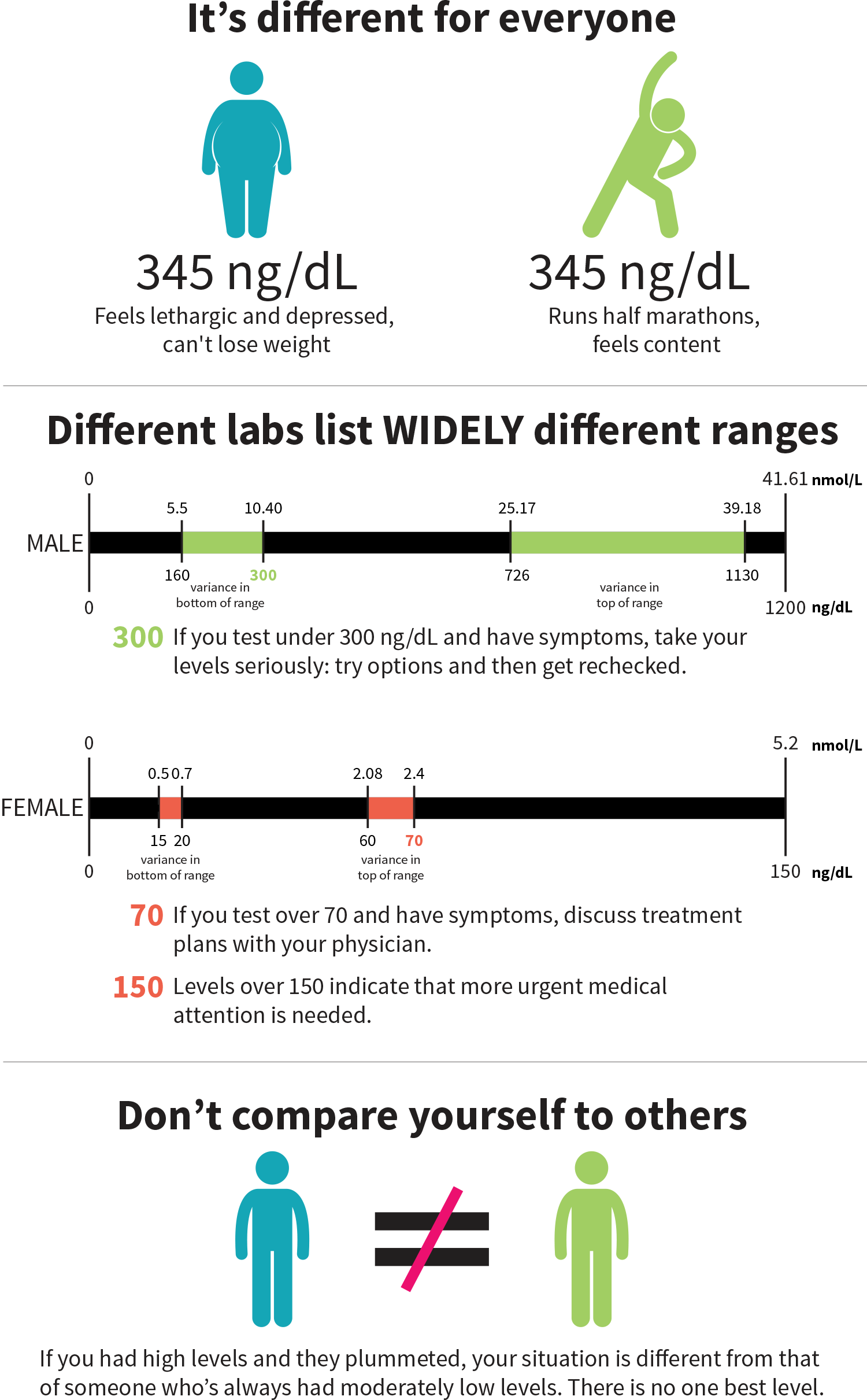
When your T levels are tested, the reference range can vary a lot from lab to lab. A recent study showed that the bottom of the range for males can be 5.55–10.4 nanomoles per liter, or nmol/L (160–300 nanograms per deciliter, or ng/dL), and the top of the range can be 25.17–39.18 nmol/L (726–1,130 ng/dL).[3] So if you get measured at 280 ng/dL, you may or may not be considered as having “low testosterone”.[3]
Because testosterone levels can fluctuate throughout the day, the test should be performed in the morning (8–11 a.m.). If the results come back low, a second test can be ordered to confirm the first result. As part of the workup, your physician may also measure your levels of luteinizing hormone (LH), follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH), and the T4 thyroid hormone (thyroxine) to get an accurate diagnosis.
Assessing testosterone levels
Examine Database: Testosterone
Research FeedRead all studies
In this meta-analysis of 11 randomized controlled trials, mostly in women, low-fat diets did not affect levels of estrogen or testosterone in the blood.
References
Examine Database References
- Royal Jelly - Morita H, Ikeda T, Kajita K, Fujioka K, Mori I, Okada H, Uno Y, Ishizuka TEffect of royal jelly ingestion for six months on healthy volunteersNutr J.(2012 Sep 21)
- Ginger - Waleed Abid Al-Kadir Mares, Wisam S. NajamThe effect of Ginger on semen parameters and serum FSH, LH & testosterone of infertile menTikrit Medical Journal.()
- DHEA - Stomati M, Monteleone P, Casarosa E, Quirici B, Puccetti S, Bernardi F, Genazzani AD, Rovati L, Luisi M, Genazzani ARSix-month oral dehydroepiandrosterone supplementation in early and late postmenopauseGynecol Endocrinol.(2000 Oct)
- D-Aspartic Acid - mma D’Aniello, Salvatore Ronsini, Tiziana Notari, Natascia Grieco, Vincenzo Infante, Nicola D’Angel, Fara Mascia, Maria Maddalena Di Fiore, George Fisher, Antimo D’AnielloD-Aspartate, a Key Element for the Improvement of Sperm QualityMedicine and Healthcare.()
- Cannabis - E B De Sousa Fernandes Perna, E L Theunissen, K P C Kuypers, S W Toennes, J G RamaekersSubjective aggression during alcohol and cannabis intoxication before and after aggression exposurePsychopharmacology (Berl).(2016 Sep)
- Red Clover Extract - Lee CC, Bloem CJ, Kasa-Vubu JZ, Liang LJEffect of oral phytoestrogen on androgenicity and insulin sensitivity in postmenopausal womenDiabetes Obes Metab.(2012 Apr)
- Tribulus Terrestris - Roaiah MF, El Khayat YI, GamalEl Din SF, Abd El Salam MAPilot Study on the Effect of Botanical Medicine (Tribulus terrestris) on Serum Testosterone Level and Erectile Function in Aging Males With Partial Androgen Deficiency (PADAM)J Sex Marital Ther.(2016 May 18)
- Ashwagandha - Gupta A, Mahdi AA, Shukla KK, Ahmad MK, Bansal N, Sankhwar P, Sankhwar SNEfficacy of Withania somnifera on seminal plasma metabolites of infertile males: a proton NMR study at 800 MHzJ Ethnopharmacol.(2013 Aug 26)
- Tribulus Terrestris - Neychev VK, Mitev VIThe aphrodisiac herb Tribulus terrestris does not influence the androgen production in young menJ Ethnopharmacol.(2005 Oct 3)
- Ashwagandha - Wankhede S, Langade D, Joshi K, Sinha SR, Bhattacharyya SExamining the effect of Withania somnifera supplementation on muscle strength and recovery: a randomized controlled trialJ Int Soc Sports Nutr.(2015 Nov 25)
- DHEA - Martina V, Benso A, Gigliardi VR, Masha A, Origlia C, Granata R, Ghigo EShort-term dehydroepiandrosterone treatment increases platelet cGMP production in elderly male subjectsClin Endocrinol (Oxf).(2006 Mar)
- D-Aspartic Acid - Darryn S. Willoughby, Brian Leutholtzd-Aspartic acid supplementation combined with 28 days of heavy resistance training has no effect on body composition, muscle strength, and serum hormones associated with the hypothalamo-pituitary-gonadal axis in resistance-trained menNutrition Research.()
- Calcium - Vedat Cinar, Abdulkerim Kasim Baltaci, Rasim Mogulkoc, Mehmet KilicTestosterone levels in athletes at rest and exhaustion: effects of calcium supplementationBiol Trace Elem Res.(Summer 2009)
- Alcohol - Välimäki MJ, Härkönen M, Eriksson CJ, Ylikahri RHSex hormones and adrenocortical steroids in men acutely intoxicated with ethanolAlcohol.(1984 Jan-Feb)
- Ecdysteroids - Wilborn CD, Taylor LW, Campbell BI, Kerksick C, Rasmussen CJ, Greenwood M, Kreider RBEffects of methoxyisoflavone, ecdysterone, and sulfo-polysaccharide supplementation on training adaptations in resistance-trained malesJ Int Soc Sports Nutr.(2006 Dec 13)
- Velvet Antler - Sleivert G, Burke V, Palmer C, Walmsley A, Gerrard D, Haines S, Littlejohn RThe effects of deer antler velvet extract or powder supplementation on aerobic power, erythropoiesis, and muscular strength and endurance characteristicsInt J Sport Nutr Exerc Metab.(2003 Sep)
- Tribulus Terrestris - Roaiah MF, Elkhayat YI, Saleh SF, Abd El Salam MAProspective Analysis on the Effect of Botanical Medicine (Tribulus terrestris) on Serum Testosterone Level and Semen Parameters in Males with Unexplained InfertilityJ Diet Suppl.(2016 Jun 23)
- Curcumin - Choi YH, Han DH, Kim SW, Kim MJ, Sung HH, Jeon HG, Jeong BC, Seo SI, Jeon SS, Lee HM, Choi HYA randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial to evaluate the role of curcumin in prostate cancer patients with intermittent androgen deprivationProstate.(2019 May)
- Panax Ginseng (Korean Ginseng) - de Andrade E, de Mesquita AA, Claro Jde A, de Andrade PM, Ortiz V, Paranhos M, Srougi MStudy of the efficacy of Korean Red Ginseng in the treatment of erectile dysfunctionAsian J Androl.(2007 Mar)
- Magnesium - Cinar V, Polat Y, Baltaci AK, Mogulkoc REffects of magnesium supplementation on testosterone levels of athletes and sedentary subjects at rest and after exhaustionBiol Trace Elem Res.(2011 Apr)
- DHEA - Muller M, van den Beld AW, van der Schouw YT, Grobbee DE, Lamberts SWEffects of dehydroepiandrosterone and atamestane supplementation on frailty in elderly menJ Clin Endocrinol Metab.(2006 Oct)
- Licorice - R A Josephs, J S Guinn, M L Harper, F AskariLiquorice consumption and salivary testosterone concentrationsLancet.(2001 Nov 10)
- Vitamin D - Elisabeth Lerchbaum, Christian Trummer, Verena Theiler-Schwetz, Martina Kollmann, Monika Wölfler, Annemieke C Heijboer, Stefan Pilz, Barbara Obermayer-PietschEffects of vitamin D supplementation on androgens in men with low testosterone levels: a randomized controlled trialEur J Nutr.(2019 Dec)
- Boron - Green NR, Ferrando AAPlasma boron and the effects of boron supplementation in malesEnviron Health Perspect.(1994 Nov)
- Red Clover Extract - Hidalgo LA, Chedraui PA, Morocho N, Ross S, San Miguel GThe effect of red clover isoflavones on menopausal symptoms, lipids and vaginal cytology in menopausal women: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled studyGynecol Endocrinol.(2005 Nov)
- Alcohol - Sierksma A, Sarkola T, Eriksson CJ, van der Gaag MS, Grobbee DE, Hendriks HFEffect of moderate alcohol consumption on plasma dehydroepiandrosterone sulfate, testosterone, and estradiol levels in middle-aged men and postmenopausal women: a diet-controlled intervention studyAlcohol Clin Exp Res.(2004 May)
- Stinging Nettle - Safarinejad MRUrtica dioica for treatment of benign prostatic hyperplasia: a prospective, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, crossover studyJ Herb Pharmacother.(2005)
- DHEA - Weiss EP, Shah K, Fontana L, Lambert CP, Holloszy JO, Villareal DTDehydroepiandrosterone replacement therapy in older adults: 1- and 2-y effects on boneAm J Clin Nutr.(2009 May)
- Tongkat Ali - Shawn M Talbott, Julie A Talbott, Annie George, and Mike PughEffect of Tongkat Ali on stress hormones and psychological mood state in moderately stressed subjectsJISSN.()
- Zinc - Netter A, Hartoma R, Nahoul KEffect of zinc administration on plasma testosterone, dihydrotestosterone, and sperm countArch Androl.(1981 Aug)
- Creatine - Volek JS, Ratamess NA, Rubin MR, Gómez AL, French DN, McGuigan MM, Scheett TP, Sharman MJ, Häkkinen K, Kraemer WJThe effects of creatine supplementation on muscular performance and body composition responses to short-term resistance training overreachingEur J Appl Physiol.(2004 May)
- Maca - Gonzales GF, Córdova A, Vega K, Chung A, Villena A, Góñez C, Castillo SEffect of Lepidium meyenii (MACA) on sexual desire and its absent relationship with serum testosterone levels in adult healthy menAndrologia.(2002 Dec)
- Vitamin D - Małgorzata Magdalena Michalczyk, Artur Gołaś, Adam Maszczyk, Piotr Kaczka, Adam ZającInfluence of Sunlight and Oral D 3 Supplementation on Serum 25(OH)D Concentration and Exercise Performance in Elite Soccer PlayersNutrients.(2020 May 4)
- 16:8 Intermittent Fasting - Tatiana Moro, Grant Tinsley, Antonino Bianco, Giuseppe Marcolin, Quirico Francesco Pacelli, Giuseppe Battaglia, Antonio Palma, Paulo Gentil, Marco Neri, Antonio PaoliEffects of eight weeks of time-restricted feeding (16/8) on basal metabolism, maximal strength, body composition, inflammation, and cardiovascular risk factors in resistance-trained malesJ Transl Med.(2016 Oct 13)
- Zinc - Kilic M, Baltaci AK, Gunay M, Gökbel H, Okudan N, Cicioglu IThe effect of exhaustion exercise on thyroid hormones and testosterone levels of elite athletes receiving oral zincNeuro Endocrinol Lett.(2006 Feb-Apr)
- DHEA - Libè R, Barbetta L, Dall'Asta C, Salvaggio F, Gala C, Beck-Peccoz P, Ambrosi BEffects of dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA) supplementation on hormonal, metabolic and behavioral status in patients with hypoadrenalismJ Endocrinol Invest.(2004 Sep)
- Beta-Alanine - Hoffman J, Ratamess NA, Ross R, Kang J, Magrelli J, Neese K, Faigenbaum AD, Wise JABeta-alanine and the hormonal response to exerciseInt J Sports Med.(2008 Dec)
- Ashwagandha - Lopresti AL, Smith SJ, Malvi H, Kodgule RAn investigation into the stress-relieving and pharmacological actions of an ashwagandha (Withania somnifera) extract: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled studyMedicine (Baltimore).(2019 Sep)
- Fenugreek - Steels E, Rao A, Vitetta LPhysiological Aspects of Male Libido Enhanced by Standardized Trigonella foenum-graecum Extract and Mineral FormulationPhytother Res.(2011 Feb 10)
- Garcinia - Hayamizu K, Tomi H, Kaneko I, Shen M, Soni MG, Yoshino GEffects of Garcinia cambogia extract on serum sex hormones in overweight subjectsFitoterapia.(2008 Jun)
- Licorice - Helga Agusta Sigurjonsdottir, Magnus Axelson, Gudmundur Johannsson, Karin Manhem, Ernst Nystrom, Sven WallerstedtLiquorice in moderate doses does not affect sex steroid hormones of biological importance although the effect differs between the gendersHorm Res.(2006)
- DHEA - Kenny AM, Boxer RS, Kleppinger A, Brindisi J, Feinn R, Burleson JADehydroepiandrosterone combined with exercise improves muscle strength and physical function in frail older womenJ Am Geriatr Soc.(2010 Sep)
- Saw Palmetto - Bent S, Kane C, Shinohara K, Neuhaus J, Hudes ES, Goldberg H, Avins ALSaw palmetto for benign prostatic hyperplasiaN Engl J Med.(2006 Feb 9)
- Tongkat Ali - M I B M Tambi, M K Imran, R R HenkelStandardised water-soluble extract of Eurycoma longifolia, Tongkat ali, as testosterone booster for managing men with late-onset hypogonadism?Andrologia.(2012 May)
- Maca - Zenico T, Cicero AF, Valmorri L, Mercuriali M, Bercovich ESubjective effects of Lepidium meyenii (Maca) extract on well-being and sexual performances in patients with mild erectile dysfunction: a randomised, double-blind clinical trialAndrologia.(2009 Apr)
- Saffron - Fukui H, Toyoshima K, Komaki RPsychological and neuroendocrinological effects of odor of saffron (Crocus sativus)Phytomedicine.(2011 Jun 15)
- Panax Ginseng (Korean Ginseng) - Salvati G, Genovesi G, Marcellini L, Paolini P, De Nuccio I, Pepe M, Re MEffects of Panax Ginseng C.A. Meyer saponins on male fertilityPanminerva Med.(1996 Dec)
- Coleus forskohlii - Godard MP, Johnson BA, Richmond SRBody composition and hormonal adaptations associated with forskolin consumption in overweight and obese menObes Res.(2005 Aug)
- L-Carnitine - G Cavallini, S Caracciolo, G Vitali, F Modenini, G BiagiottiCarnitine versus androgen administration in the treatment of sexual dysfunction, depressed mood, and fatigue associated with male agingUrology.(2004 Apr)
- Colostrum - Shing CM, Peake JM, Suzuki K, Jenkins DG, Coombes JSA pilot study: bovine colostrum supplementation and hormonal and autonomic responses to competitive cyclingJ Sports Med Phys Fitness.(2013 Oct)
- Alcohol - Sarkola T, Fukunaga T, Mäkisalo H, Peter Eriksson CJAcute effect of alcohol on androgens in premenopausal womenAlcohol Alcohol.(2000 Jan)
- DHEA - Yamada S, Akishita M, Fukai S, Ogawa S, Yamaguchi K, Matsuyama J, Kozaki K, Toba K, Ouchi YEffects of dehydroepiandrosterone supplementation on cognitive function and activities of daily living in older women with mild to moderate cognitive impairmentGeriatr Gerontol Int.(2010 Oct)
- Maca - Melnikovova I, Fait T, Kolarova M, Fernandez EC, Milella LEffect of Lepidium meyenii Walp. on Semen Parameters and Serum Hormone Levels in Healthy Adult Men: A Double-Blind, Randomized, Placebo-Controlled Pilot StudyEvid Based Complement Alternat Med.(2015)
- D-Aspartic Acid - Topo E, Soricelli A, D'Aniello A, Ronsini S, D'Aniello GThe role and molecular mechanism of D-aspartic acid in the release and synthesis of LH and testosterone in humans and ratsReprod Biol Endocrinol.(2009 Oct 27)
- DHEA - Morales A, Black A, Emerson L, Barkin J, Kuzmarov I, Day AAndrogens and sexual function: a placebo-controlled, randomized, double-blind study of testosterone vs. dehydroepiandrosterone in men with sexual dysfunction and androgen deficiencyAging Male.(2009 Dec)
- Arginine - Abel T, Knechtle B, Perret C, Eser P, von Arx P, Knecht HInfluence of chronic supplementation of arginine aspartate in endurance athletes on performance and substrate metabolism - a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled studyInt J Sports Med.(2005 Jun)
- DHEA - Ostojic SM, Calleja J, Jourkesh MEffects of short-term dehydroepiandrosterone supplementation on body composition in young athletesChin J Physiol.(2010 Feb 28)
- DHEA - Jedrzejuk D, Medras M, Milewicz A, Demissie MDehydroepiandrosterone replacement in healthy men with age-related decline of DHEA-S: effects on fat distribution, insulin sensitivity and lipid metabolismAging Male.(2003 Sep)
- Vitamin D - Juan Mielgo-Ayuso, Julio Calleja-González, Aritz Urdampilleta, Patxi León-Guereño, Alfredo Córdova, Alberto Caballero-García, Diego Fernandez-LázaroEffects of Vitamin D Supplementation on Haematological Values and Muscle Recovery in Elite Male Traditional RowersNutrients.(2018 Dec 12)
- Coenzyme Q10 - Izadi A, Ebrahimi S, Shirazi S, Taghizadeh S, Parizad M, Farzadi L, Gargari BPHormonal and Metabolic Effects of Coenzyme Q10 and/or Vitamin E in Patients With Polycystic Ovary SyndromeJ Clin Endocrinol Metab.(2019 Feb 1)
- Zinc - Kilic MEffect of fatiguing bicycle exercise on thyroid hormone and testosterone levels in sedentary males supplemented with oral zincNeuro Endocrinol Lett.(2007 Oct)
- Boron - Naghii MR, Mofid M, Asgari AR, Hedayati M, Daneshpour MSComparative effects of daily and weekly boron supplementation on plasma steroid hormones and proinflammatory cytokinesJ Trace Elem Med Biol.(2011 Jan)
- Tribulus Terrestris - de Souza KZ, Vale FB, Geber SEfficacy of Tribulus terrestris for the treatment of hypoactive sexual desire disorder in postmenopausal women: a randomized, double-blinded, placebo-controlled trialMenopause.(2016 Nov)
- Licorice - Armanini D, Bonanni G, Palermo MReduction of serum testosterone in men by licoriceN Engl J Med.(1999 Oct 7)
- Tribulus Terrestris - Sellandi TM, Thakar AB, Baghel MSClinical study of Tribulus terrestris Linn. in Oligozoospermia: A double blind studyAyu.(2012 Jul)
- Boron - Nielsen FH, Hunt CD, Mullen LM, Hunt JREffect of dietary boron on mineral, estrogen, and testosterone metabolism in postmenopausal womenFASEB J.(1987 Nov)
- Yohimbine - Guay AT, Spark RF, Jacobson J, Murray FT, Geisser MEYohimbine treatment of organic erectile dysfunction in a dose-escalation trialInt J Impot Res.(2002 Feb)
- Vitamin D - Armin Zittermann, Jana B Ernst, Sylvana Prokop, Uwe Fuchs, Jens Dreier, Joachim Kuhn, Cornelius Knabbe, Heiner K Berthold, Ioanna Gouni-Berthold, Jan F Gummert, Jochen Börgermann, Stefan PilzVitamin D supplementation does not prevent the testosterone decline in males with advanced heart failure: the EVITA trialEur J Nutr.(2019 Mar)
- HMB - Wilson JM, Lowery RP, Joy JM, Walters JA, Baier SM, Fuller JC, Stout JR, Norton LE, Sikorski EM, Wilson SM, Duncan NM, Zanchi NE, Rathmacher Jβ-Hydroxy-β-methylbutyrate free acid reduces markers of exercise-induced muscle damage and improves recovery in resistance-trained menBr J Nutr.(2013 Jan 3)
- Creatine - van der Merwe J, Brooks NE, Myburgh KHThree weeks of creatine monohydrate supplementation affects dihydrotestosterone to testosterone ratio in college-aged rugby playersClin J Sport Med.(2009 Sep)
- Tribulus Terrestris - Rogerson S, Riches CJ, Jennings C, Weatherby RP, Meir RA, Marshall-Gradisnik SMThe effect of five weeks of Tribulus terrestris supplementation on muscle strength and body composition during preseason training in elite rugby league playersJ Strength Cond Res.(2007 May)
- Licorice - Armanini D, Bonanni G, Mattarello MJ, Fiore C, Sartorato P, Palermo MLicorice consumption and serum testosterone in healthy manExp Clin Endocrinol Diabetes.(2003 Sep)
- Caffeine - Beaven CM, Hopkins WG, Hansen KT, Wood MR, Cronin JB, Lowe TEDose effect of caffeine on testosterone and cortisol responses to resistance exerciseInt J Sport Nutr Exerc Metab.(2008 Apr)
- Saffron - Safarinejad MR, Shafiei N, Safarinejad SA prospective double-blind randomized placebo-controlled study of the effect of saffron (Crocus sativus Linn.) on semen parameters and seminal plasma antioxidant capacity in infertile men with idiopathic oligoasthenoteratozoospermiaPhytother Res.(2011 Apr)
- DHEA - Igwebuike A, Irving BA, Bigelow ML, Short KR, McConnell JP, Nair KSLack of dehydroepiandrosterone effect on a combined endurance and resistance exercise program in postmenopausal womenJ Clin Endocrinol Metab.(2008 Feb)
- Korean black raspberry - Ji Eun Lee, Eunkyo Park, Jung Eun Lee, Joong Hyuck Auh, Hyung-Kyoon Choi, Jaehwi Lee, Soomuk Cho, Jung-Hyun KimEffects of a Rubus coreanus Miquel supplement on plasma antioxidant capacity in healthy Korean menNutr Res Pract.(2011 Oct)
- Phosphatidylserine - Parker AG, Gordon J, Thornton A, Byars A, Lubker J, Bartlett M, Byrd M, Oliver J, Simbo S, Rasmussen C, Greenwood M, Kreider RBThe effects of IQPLUS Focus on cognitive function, mood and endocrine response before and following acute exerciseJ Int Soc Sports Nutr.(2011 Oct 21)
- Alcohol - Mendelson JH, Mello NK, Ellingboe JEffects of acute alcohol intake on pituitary-gonadal hormones in normal human malesJ Pharmacol Exp Ther.(1977 Sep)
- DHEA - Liu TC, Lin CH, Huang CY, Ivy JL, Kuo CHEffect of acute DHEA administration on free testosterone in middle-aged and young men following high-intensity interval trainingEur J Appl Physiol.(2013 Feb 17)
- D-Aspartic Acid - Melville GW, Siegler JC, Marshall PWThree and six grams supplementation of d-aspartic acid in resistance trained menJ Int Soc Sports Nutr.(2015 Apr 1)
- DHEA - Alessandro D Genazzani, Massimo Stomati, Francesca Bernardi, Matteo Pieri, Lucio Rovati, Andrea R GenazzaniLong-term low-dose dehydroepiandrosterone oral supplementation in early and late postmenopausal women modulates endocrine parameters and synthesis of neuroactive steroidsFertil Steril.(2003 Dec)
- Caffeine - Cook C, Beaven CM, Kilduff LP, Drawer SAcute caffeine ingestion increases voluntarily chosen resistance training load following limited sleepInt J Sport Nutr Exerc Metab.(2012 Feb 15)
- Zinc - Ghanbarali Raeis Jalali, Jamshid Roozbeh, Azam Mohammadzadeh, Maryam Sharifian, Mohammad Mahdi Sagheb, Alireza Hamidian Jahromi, Sanaz Shabani, Fariborz Ghaffarpasand, Raha AfsharianiImpact of oral zinc therapy on the level of sex hormones in male patients on hemodialysisRen Fail.(2010 May)
- Vitamin D - Amirhossein Ramezani Ahmadi, Majid Mohammadshahi, Aliakbar Alizadeh, Kambiz Ahmadi Angali, Alireza JahanshahiEffects of vitamin D3 supplementation for 12 weeks on serum levels of anabolic hormones, anaerobic power, and aerobic performance in active male subjects: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trialEur J Sport Sci.(2020 Nov)
- Panax Ginseng (Korean Ginseng) - E. Azizi, F. MoradiThe effect of ginseng supplementation on anabolic index, muscle strength, body composition, and testosterone and cortisol response to acute resistance exercise in male bodybuildersDepartment of Physical Education and Sport Sciences.()
- Alcohol - W R Phipps, S E Lukas, J H Mendelson, J Ellingboe, S L Palmieri, I SchiffAcute ethanol administration enhances plasma testosterone levels following gonadotropin stimulation in menPsychoneuroendocrinology.(1987)
- Maca - Gonzales GF, Córdova A, Vega K, Chung A, Villena A, Góñez CEffect of Lepidium meyenii (Maca), a root with aphrodisiac and fertility-enhancing properties, on serum reproductive hormone levels in adult healthy menJ Endocrinol.(2003 Jan)
- Alcohol - Sarkola T, Eriksson CJTestosterone increases in men after a low dose of alcoholAlcohol Clin Exp Res.(2003 Apr)
- Velvet Antler - Syrotuik DG, MacFadyen KL, Harber VJ, Bell GJEffect of elk velvet antler supplementation on the hormonal response to acute and chronic exercise in male and female rowersInt J Sport Nutr Exerc Metab.(2005 Aug)
- Grape Seed Extract - Ikuko Kijima, Sheryl Phung, Gene Hur, Sum-Ling Kwok, Shiuan ChenGrape seed extract is an aromatase inhibitor and a suppressor of aromatase expressionCancer Res.(2006 Jun 1)
- Coenzyme Q10 - Safarinejad MREfficacy of coenzyme Q10 on semen parameters, sperm function and reproductive hormones in infertile menJ Urol.(2009 Jul)
- DHEA - Genazzani AR, Pluchino N, Begliuomini S, Stomati M, Bernardi F, Pieri M, Casarosa E, Palumbo M, Genazzani AD, Luisi MLong-term low-dose oral administration of dehydroepiandrosterone modulates adrenal response to adrenocorticotropic hormone in early and late postmenopausal womenGynecol Endocrinol.(2006 Nov)
- Caffeine - Gillingham R, Keefe AA, Keillor J, Tikuisis PEffect of caffeine on target detection and rifle marksmanshipErgonomics.(2003 Dec 15)
- DHEA - Wallace MB, Lim J, Cutler A, Bucci LEffects of dehydroepiandrosterone vs androstenedione supplementation in menMed Sci Sports Exerc.(1999 Dec)
- DHEA - Dayal M, Sammel MD, Zhao J, Hummel AC, Vandenbourne K, Barnhart KTSupplementation with DHEA: effect on muscle size, strength, quality of life, and lipidsJ Womens Health (Larchmt).(2005 Jun)
- Astaxanthin - Comhaire FH, El Garem Y, Mahmoud A, Eertmans F, Schoonjans FCombined conventional/antioxidant "Astaxanthin" treatment for male infertility: a double blind, randomized trialAsian J Androl.(2005 Sep)
- L-Carnitine - Kraemer WJ, Volek JS, French DN, Rubin MR, Sharman MJ, Gómez AL, Ratamess NA, Newton RU, Jemiolo B, Craig BW, Häkkinen KThe effects of L-carnitine L-tartrate supplementation on hormonal responses to resistance exercise and recoveryJ Strength Cond Res.(2003 Aug)
- Green Tea Extract - Wu AH, Spicer D, Stanczyk FZ, Tseng CC, Yang CS, Pike MCEffect of 2-month controlled green tea intervention on lipoprotein cholesterol, glucose, and hormone levels in healthy postmenopausal womenCancer Prev Res (Phila).(2012 Mar)
- Ashwagandha - Abbas Ali Mahdi, Kamla Kant Shukla, Mohammad Kaleem Ahmad, Singh Rajender, Satya Narain Shankhwar, Vishwajeet Singh, Deepansh DalelaWithania somnifera Improves Semen Quality in Stress-Related Male FertilityEvid Based Complement Alternat Med.(2009 Sep 29)
- Nicotine - Mendelson JH, Sholar MB, Mutschler NH, Jaszyna-Gasior M, Goletiani NV, Siegel AJ, Mello NKEffects of intravenous cocaine and cigarette smoking on luteinizing hormone, testosterone, and prolactin in menJ Pharmacol Exp Ther.(2003 Oct)
- Caffeine - Paton CD, Lowe T, Irvine ACaffeinated chewing gum increases repeated sprint performance and augments increases in testosterone in competitive cyclistsEur J Appl Physiol.(2010 Dec)
- DHEA - Brown GA, Vukovich MD, Sharp RL, Reifenrath TA, Parsons KA, King DSEffect of oral DHEA on serum testosterone and adaptations to resistance training in young menJ Appl Physiol.(1999 Dec)
- Alcohol - Barnes MJ, Mundel T, Stannard SRThe effects of acute alcohol consumption on recovery from a simulated rugby matchJ Sports Sci.(2012)
- Vitamin D - Pilz S, Frisch S, Koertke H, Kuhn J, Dreier J, Obermayer-Pietsch B, Wehr E, Zittermann AEffect of vitamin D supplementation on testosterone levels in menHorm Metab Res.(2011 Mar)
- Vitamin D - Michelle S Rockwell, Madlyn I Frisard, Janet W Rankin, Jennifer S Zabinsky, Ryan P Mcmillan, Wen You, Kevin P Davy, Matthew W HulverEffects of Seasonal Vitamin D3 Supplementation on Strength, Power, and Body Composition in College SwimmersInt J Sport Nutr Exerc Metab.(2020 Feb 4)
- Saw Palmetto - Strauch G, Perles P, Vergult G, Gabriel M, Gibelin B, Cummings S, Malbecq W, Malice MPComparison of finasteride (Proscar) and Serenoa repens (Permixon) in the inhibition of 5-alpha reductase in healthy male volunteersEur Urol.(1994)
- Creatine - Schilling BK, Stone MH, Utter A, Kearney JT, Johnson M, Coglianese R, Smith L, O'Bryant HS, Fry AC, Starks M, Keith R, Stone MECreatine supplementation and health variables: a retrospective studyMed Sci Sports Exerc.(2001 Feb)
- Colostrum - A Mero, H Miikkulainen, J Riski, R Pakkanen, J Aalto, T TakalaEffects of bovine colostrum supplementation on serum IGF-I, IgG, hormone, and saliva IgA during trainingJ Appl Physiol (1985).(1997 Oct)
- Punicalagins - Pantuck AJ, Leppert JT, Zomorodian N, Aronson W, Hong J, Barnard RJ, Seeram N, Liker H, Wang H, Elashoff R, Heber D, Aviram M, Ignarro L, Belldegrun APhase II study of pomegranate juice for men with rising prostate-specific antigen following surgery or radiation for prostate cancerClin Cancer Res.(2006 Jul 1)
- Chromium - Lydic ML, McNurlan M, Bembo S, Mitchell L, Komaroff E, Gelato MChromium picolinate improves insulin sensitivity in obese subjects with polycystic ovary syndromeFertil Steril.(2006 Jul)
- Licorice - Decio Armanini, Mee Jung Mattarello, Cristina Fiore, Guglielmo Bonanni, Carla Scaroni, Paola Sartorato, Mario PalermoLicorice reduces serum testosterone in healthy womenSteroids.(Oct-Nov 2004)
- 7-Keto DHEA - Douglas S. Kaiman, Carlon M. Colker, Melissa A. Swain, Georgeann C. Torina, Qiuhu ShiA randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study of 3-acetyl-7-oxo-dehydroepiandrosterone in healthy overweight adultsCurrent Therapeutic Research.()
- Fish Oil - Vargas ML, Almario RU, Buchan W, Kim K, Karakas SEMetabolic and endocrine effects of long-chain versus essential omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids in polycystic ovary syndromeMetabolism.(2011 Dec)
- 16:8 Intermittent Fasting - Matthew T Stratton, Grant M Tinsley, Michaela G Alesi, Garrett M Hester, Alex A Olmos, Paul R Serafini, Andrew S Modjeski, Gerald T Mangine, Kelsey King, Shelby N Savage, Austin T Webb, Trisha A VanDusseldorpFour Weeks of Time-Restricted Feeding Combined with Resistance Training Does Not Differentially Influence Measures of Body Composition, Muscle Performance, Resting Energy Expenditure, and Blood BiomarkersNutrients.(2020 Apr 17)
- Vitamin D - Soma Saha, Ravinder Goswami, Lakshmy Ramakrishnan, Sreenivas Vishnubhatla, Samrina Mahtab, Parmita Kar, Sunita Srinivasan, Namrata Singh, Upinderpal SinghVitamin D and calcium supplementation, skeletal muscle strength and serum testosterone in young healthy adult males: Randomized control trialClin Endocrinol (Oxf).(2018 Feb)
- Rhodiola Rosea - Jówko E, Sadowski J, Długołęcka B, Gierczuk D, Opaszowski B, Cieśliński IEffects of Rhodiola rosea supplementation on mental performance, physical capacity, and oxidative stress biomarkers in healthy menJ Sport Health Sci.(2018 Oct)
- HMB - Hoffman JR, Cooper J, Wendell M, Im J, Kang JEffects of beta-hydroxy beta-methylbutyrate on power performance and indices of muscle damage and stress during high-intensity trainingJ Strength Cond Res.(2004 Nov)
- Alcohol - Low plasma testosterone values in men during hangoverJournal of Steroid Biochemistry.()
- Tribulus Terrestris - Saudan C, Baume N, Emery C, Strahm E, Saugy MShort term impact of Tribulus terrestris intake on doping control analysis of endogenous steroidsForensic Sci Int.(2008 Jun 10)
- Arachidonic Acid - Roberts MD, Iosia M, Kerksick CM, Taylor LW, Campbell B, Wilborn CD, Harvey T, Cooke M, Rasmussen C, Greenwood M, Wilson R, Jitomir J, Willoughby D, Kreider RBEffects of arachidonic acid supplementation on training adaptations in resistance-trained malesJ Int Soc Sports Nutr.(2007 Nov 28)
- Gamma Oryzanol - Fry AC, Bonner E, Lewis DL, Johnson RL, Stone MH, Kraemer WJThe effects of gamma-oryzanol supplementation during resistance exercise trainingInt J Sport Nutr.(1997 Dec)
- Reishi - Noguchi M, Kakuma T, Tomiyasu K, Yamada A, Itoh K, Konishi F, Kumamoto S, Shimizu K, Kondo R, Matsuoka KRandomized clinical trial of an ethanol extract of Ganoderma lucidum in men with lower urinary tract symptomsAsian J Androl.(2008 Sep)
- Velvet Antler - Conaglen HM, Suttie JM, Conaglen JVEffect of deer velvet on sexual function in men and their partners: a double-blind, placebo-controlled studyArch Sex Behav.(2003 Jun)
- Chrysin - Gambelunghe C, Rossi R, Sommavilla M, Ferranti C, Rossi R, Ciculi C, Gizzi S, Micheletti A, Rufini SEffects of chrysin on urinary testosterone levels in human malesJ Med Food.(2003 Winter)
- Ashwagandha - Adrian L Lopresti, Peter D Drummond, Stephen J SmithA Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled, Crossover Study Examining the Hormonal and Vitality Effects of Ashwagandha ( Withania somnifera) in Aging, Overweight MalesAm J Mens Health.(Mar-Apr 2019)
- HMB - Portal S, Zadik Z, Rabinowitz J, Pilz-Burstein R, Adler-Portal D, Meckel Y, Cooper DM, Eliakim A, Nemet DThe effect of HMB supplementation on body composition, fitness, hormonal and inflammatory mediators in elite adolescent volleyball players: a prospective randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled studyEur J Appl Physiol.(2011 Sep)
- Licorice - Mee Jung Mattarello, Stefano Benedini, Cristina Fiore, Valentina Camozzi, Paola Sartorato, Giovanni Luisetto, Decio ArmaniniEffect of licorice on PTH levels in healthy womenSteroids.(2006 May)
- Alcohol - Koziris LP, Kraemer WJ, Gordon SE, Incledon T, Knuttgen HGEffect of acute postexercise ethanol intoxication on the neuroendocrine response to resistance exerciseJ Appl Physiol.(2000 Jan)
- Shilajit - Biswas TK, Pandit S, Mondal S, Biswas SK, Jana U, Ghosh T, Tripathi PC, Debnath PK, Auddy RG, Auddy BClinical evaluation of spermatogenic activity of processed Shilajit in oligospermiaAndrologia.(2010 Feb)
- Alanylglutamine - Hoffman JR, Ratamess NA, Kang J, Rashti SL, Kelly N, Gonzalez AM, Stec M, Anderson S, Bailey BL, Yamamoto LM, Hom LL, Kupchak BR, Faigenbaum AD, Maresh CMExamination of the efficacy of acute L-alanyl-L-glutamine ingestion during hydration stress in endurance exerciseJ Int Soc Sports Nutr.(2010 Feb 3)
- Ashwagandha - Ahmad MK, Mahdi AA, Shukla KK, Islam N, Rajender S, Madhukar D, Shankhwar SN, Ahmad SWithania somnifera improves semen quality by regulating reproductive hormone levels and oxidative stress in seminal plasma of infertile malesFertil Steril.(2010 Aug)
- Ashwagandha - Ambiye VR, Langade D, Dongre S, Aptikar P, Kulkarni M, Dongre AClinical Evaluation of the Spermatogenic Activity of the Root Extract of Ashwagandha (Withania somnifera) in Oligospermic Males: A Pilot StudyEvid Based Complement Alternat Med.(2013)
- Creatine - D. Sheikholeslami Vatania, H. Farajib, R. Sooric, M. MogharnasidThe effects of creatine supplementation on performance and hormonal response in amateur swimmersScience and Sports.()
- Creatine - Hoffman J, Ratamess N, Kang J, Mangine G, Faigenbaum A, Stout JEffect of creatine and beta-alanine supplementation on performance and endocrine responses in strength/power athletesInt J Sport Nutr Exerc Metab.(2006 Aug)
- Fenugreek - Wilborn C, Taylor L, Poole C, Foster C, Willoughby D, Kreider REffects of a purported aromatase and 5α-reductase inhibitor on hormone profiles in college-age menInt J Sport Nutr Exerc Metab.(2010 Dec)
- Red Clover Extract - Imhof M, Gocan A, Reithmayr F, Lipovac M, Schimitzek C, Chedraui P, Huber JEffects of a red clover extract (MF11RCE) on endometrium and sex hormones in postmenopausal womenMaturitas.(2006 Aug 20)
- Glutamine - Rotovnik Kozjek N, Kompan L, Soeters P, Oblak I, Mlakar Mastnak D, Možina B, Zadnik V, Anderluh F, Velenik VOral glutamine supplementation during preoperative radiochemotherapy in patients with rectal cancer: a randomised double blinded, placebo controlled pilot studyClin Nutr.(2011 Oct)
- Fenugreek - Brandon Bushey, Lem W. Taylor, Colin W. Wilborn, Chris Poole, Cliffa A. Foster, Bill Campbell, Richard B. Kreider, Darryn S. WilloughbyFenugreek Extract Supplementation Has No effect on the Hormonal Profile of Resitance-Trained MalesInternational Journal of Exercise Science.()
- Creatine - Cook CJ, Crewther BT, Kilduff LP, Drawer S, Gaviglio CMSkill execution and sleep deprivation: effects of acute caffeine or creatine supplementation - a randomized placebo-controlled trialJ Int Soc Sports Nutr.(2011 Feb 16)
- Tribulus Terrestris - Kamenov Z, Fileva S, Kalinov K, Jannini EAEvaluation of the efficacy and safety of Tribulus terrestris in male sexual dysfunction-A prospective, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trialMaturitas.(2017 May)
- Tongkat Ali - Ismail SB, Wan Mohammad WM, George A, Nik Hussain NH, Musthapa Kamal ZM, Liske ERandomized Clinical Trial on the Use of PHYSTA Freeze-Dried Water Extract of Eurycoma longifolia for the Improvement of Quality of Life and Sexual Well-Being in MenEvid Based Complement Alternat Med.(2012)
- Magnesium - Farsinejad-Marj M, Azadbakht L, Mardanian F, Saneei P, Esmaillzadeh AClinical and Metabolic Responses to Magnesium Supplementation in Women with Polycystic Ovary Syndrome.Biol Trace Elem Res.(2020-Aug)
- Magnesium - Mohammad Alizadeh, Majid Karandish, Mohammad Asghari Jafarabadi, Lida Heidari, Roshan Nikbakht, Hossein Babaahmadi Rezaei, Reihaneh MousaviMetabolic and hormonal effects of melatonin and/or magnesium supplementation in women with polycystic ovary syndrome: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trialNutr Metab (Lond).(2021 Jun 6)
- Tongkat Ali - Leisegang K, Finelli R, Sikka SC, Panner Selvam MK(Jack) Improves Serum Total Testosterone in Men: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Clinical Trials.Medicina (Kaunas).(2022-Aug-04)
- Tongkat Ali - Chan KQ, Stewart C, Chester N, Hamzah SH, Yusof AThe effect of Eurycoma Longifolia on the regulation of reproductive hormones in young males.Andrologia.(2021-May)
- Tongkat Ali - Sasikala M Chinnappan, Annie George, Pragya Pandey, Govinda Narke, Yogendra Kumar ChoudharyEffect of Eurycoma longifolia standardised aqueous root extract-Physta ® on testosterone levels and quality of life in ageing male subjects: a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled multicentre studyFood Nutr Res.(2021 May 19)
- Tongkat Ali - Henkel RR, Wang R, Bassett SH, Chen T, Liu N, Zhu Y, Tambi MITongkat Ali as a potential herbal supplement for physically active male and female seniors--a pilot study.Phytother Res.(2014-Apr)
- Berberine - Xie L, Zhang D, Ma H, He H, Xia Q, Shen W, Chang H, Deng Y, Wu Q, Cong J, Wang CC, Wu XThe Effect of Berberine on Reproduction and Metabolism in Women with Polycystic Ovary Syndrome: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Control Trials.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med.(2019)
- N-Acetylcysteine - Zahra Shahveghar Asl, Karim Parastouei, Eslam EskandariThe effects of N-acetylcysteine on ovulation and sex hormones profile in women with polycystic ovary syndrome: a systematic review and meta-analysisBr J Nutr.(2023 Jan 4)
- Inositol - Greff D, Juhász AE, Váncsa S, Váradi A, Sipos Z, Szinte J, Park S, Hegyi P, Nyirády P, Ács N, Várbíró S, Horváth EMInositol is an effective and safe treatment in polycystic ovary syndrome: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.Reprod Biol Endocrinol.(2023-Jan-26)
- Chromium - Tang XL, Sun Z, Gong LChromium supplementation in women with polycystic ovary syndrome: Systematic review and meta-analysisJ Obstet Gynaecol Res.(2018 Jan)
- Red Clover Extract - Katharine E Reed, Juliana Camargo, Jill Hamilton-Reeves, Mindy Kurzer, Mark MessinaNeither soy nor isoflavone intake affects male reproductive hormones: An expanded and updated meta-analysis of clinical studiesReprod Toxicol.(2021 Mar)
- DHEA - Marina L, Sojat AS, Maseroli E, Spaggiari G, Pandurevic S, Santi DHormonal profile of menopausal women receiving androgen replacement therapy: a meta-analysis.J Endocrinol Invest.(2020-Jun)
- DHEA - Hu Y, Wan P, An X, Jiang GImpact of dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA) supplementation on testosterone concentrations and BMI in elderly women: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.Complement Ther Med.(2021-Jan)
- DHEA - Li Y, Ren J, Li N, Liu J, Tan SC, Low TY, Ma ZA dose-response and meta-analysis of dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA) supplementation on testosterone levels: perinatal prediction of randomized clinical trials.Exp Gerontol.(2020-Nov)
- DHEA - Giovanni Corona, Giulia Rastrelli, Vito A Giagulli, Annamaria Sila, Alessandra Sforza, Gianni Forti, Edoardo Mannucci, Mario MaggiDehydroepiandrosterone supplementation in elderly men: a meta-analysis study of placebo-controlled trialsJ Clin Endocrinol Metab.(2013 Sep)
- Coenzyme Q10 - Tianqing Zhang, Qi He, Hao Xiu, ZiZhu Zhang, Yao Liu, Zhenrong Chen, Hengjing HuEfficacy and Safety of Coenzyme Q10 Supplementation in the Treatment of Polycystic Ovary Syndrome: a Systematic Review and Meta-analysisReprod Sci.(2022 Aug 8)
- Resveratrol - Ali Fadlalmola H, Elhusein AM, Al-Sayaghi KM, Albadrani MS, Swamy DV, Mamanao DM, El-Amin EI, Ibrahim SE, Abbas SMEfficacy of resveratrol in women with polycystic ovary syndrome: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials.Pan Afr Med J.(2023)
- Resveratrol - Larik MO, Ahmed A, Khan L, Iftekhar MAEffects of resveratrol on polycystic ovarian syndrome: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.Endocrine.(2024-Jan)
- Ketogenic Diet - Joseph Whittaker, Miranda HarrisLow-carbohydrate diets and men's cortisol and testosterone: Systematic review and meta-analysisNutr Health.(2022 Mar 7)
- Ketogenic Diet - Furini C, Spaggiari G, Simoni M, Greco C, Santi DKetogenic state improves testosterone serum levels-results from a systematic review and meta-analysis.Endocrine.(2022-Sep-23)
- Flaxseed - Musazadeh V, Nazari A, Natami M, Hajhashemy Z, Kazemi KS, Torabi F, Moridpour AH, Vajdi M, Askari GThe effect of flaxseed supplementation on sex hormone profile in adults: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Front Nutr.(2023)
- Probiotics - Ljunggren L, Butler E, Axelsson J, Åström M, Ohlsson LEffects of probiotic supplementation on testosterone levels in healthy ageing men: A 12-week double-blind, placebo-controlled randomized clinical trial.Contemp Clin Trials Commun.(2024 Jun)
- Magnesium - Abu-Zaid A, Alzayed MM, Albahrani SJ, Almaqhawi A, Al Shaikh MA, Baradwan S, Almudiheem NA, Abuzaid M, Adly HM, Saleh SAK, Alomar ODoes Magnesium Affect Sex Hormones and Cardiometabolic Risk Factors in Patients with PCOS? Findings from a Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Medicina (Kaunas).(2025 Feb 6)
- Flavonoids - Azis A, Islam AA, Rasyid H, Hakim L, Bakri S, Bukhari A, Zainuddin AAThe effect of flavonoid and subclasses supplementation on prostate specific antigen, hormonal parameters and prostate cancer risk: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.Arch Ital Urol Androl.(2025 Apr 17)


